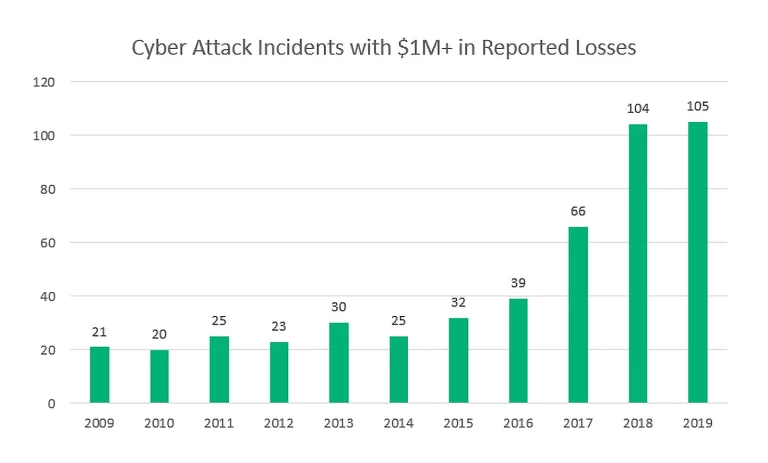
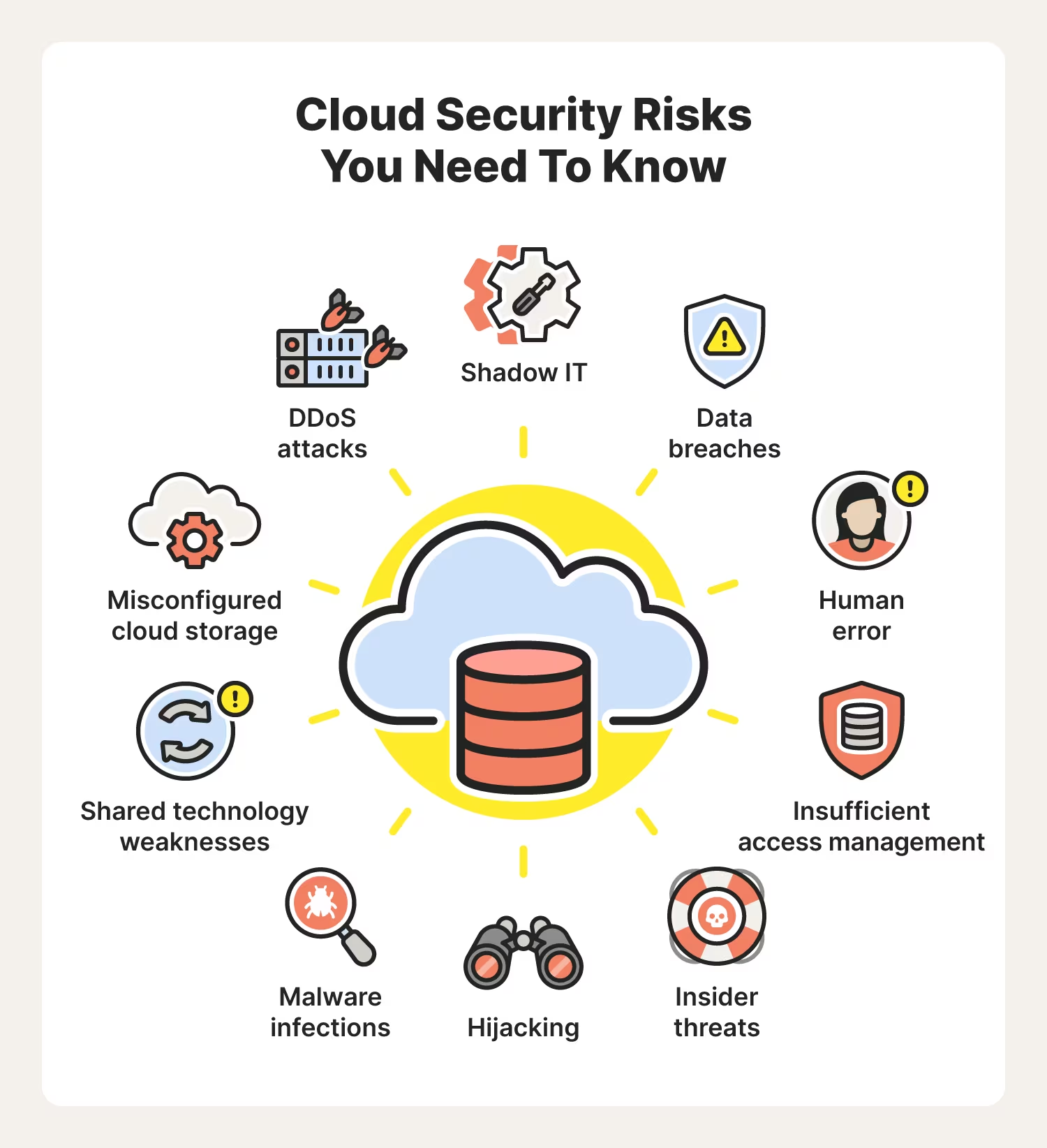
The Growing Data Protection Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
With the world becoming increasingly embedded with artificial intelligence (AI), new and urgent data protection challenges need to be addressed. The amount of total data doubles every two years, with quintillions of bytes generated every day. With the deployment of 5G networks and eventually quantum computing, this explosion will grow even faster–and substantially add to the total amount.
Streams of data from devices store information of every aspect of our lives, putting privacy in the spotlight as a global public policy issue. AI will only accelerate this trend we’re seeing, making protection even more critical. After all, a lot of the most privacy-sensitive data analysis, including AdTech networks, recommendation engines, and search algorithms, – are driven by AI. As AI evolves, and the power and speed of personal information analysis increases, the potential intrusions into our privacy become more serious.
Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition on personal devices has progressed rapidly and is now being deployed in cities and airports across America. China and other countries’ use of this technology as an authoritarian tool, has led to opposition and calls for it to be banned.
Due to concerns over facial recognition and its intrusions on privacy, the cities of Oakland, Berkeley, and San Francisco in California, as well as Brookline, Cambridge, Northampton, and Somerville in Massachusetts, have banned the technology. Meanwhile, California, New Hampshire, and Oregon have all banned the use of facial recognition capabilities added to police body cameras.
Vulnerability to Attacks
If someone carries out an adversarial attack on an AI system, this could completely confuse the system. For instance, image recognition systems have weaknesses that are extremely vulnerable.
Research has shown that even when an AI system is applied to thousands of images, a carefully placed pixel can fundamentally change how the AI system perceives that image, leading to a false prediction. This could have a serious effect on the identification of individuals, particularly pertaining to criminal activity. An AI-driven security camera might misidentify an offender, potentially leading to the wrong person getting convicted.
Trust
A significant barrier to adopting AI in a healthcare setting is trust. Patients don’t know if they can trust new software, especially when no one can explain, in layman’s terms, how that software works.Additionally, doctors may have doubts which of the many AI-driven applications have been properly coded or calibrated, or even if they have been based on physician input and accurate data.
Legislative Challenges
A key challenge for Congress is to pass privacy legislation that protects individuals against intrusions into their privacy resulting from AI, without restricting AI development. As a result, there is a certain tension between privacy concerns and the benefits provided to us by AI.
In addition, there are the many legal issues and challenges that arise when applying General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to AI:
- Transparency: this means giving people clear information about how their personal data is collected and processed using AI, as well as any impact this might have on their privacy. However, processing is unlikely to be transparent if AI systems use personal data in unexpected ways. An example includes the use of social media data for credit scoring. Transparency should include algorithmic transparency, ensuring people are made aware of how algorithms work, partnered with controls working correctly.
- Data minimization: enterprises need to minimize the quantity of data they collect and process. This can prove difficult, though, when AI tends to work on massive datasets. For this reason, organizations must express, at the outset, why they need to collect and process specific datasets.
- Fairness vs. bias: there are risks that algorithmic decisions may be mistaken or discriminatory. This is particularly the case when the outcome depends on using special category features like race, ethnicity, or gender. Moreover, an AI system’s outcome could be discriminatory if it disproportionately affects certain groups without a justifiable reason.
Protecting Personal Data in an AI World
There are several measures that should be adopted if we want to utilize AI in a way that doesn’t jeopardize our privacy:
- Privacy notices that provide clarity about what data is collected, how it will be utilized, and for what purpose. As we have seen, the use of AI systems makes this measure particularly challenging.
- Greater rights for individuals to control how organizations use their data, including rights to have their data deleted and ported.
- Data protection impact assessments to ensure that the implementation of any AI technology will be GDPR compliant.
- Privacy by design so that data protection is built into the design of any new AI system, rather than being a retro-fitted task after the system has been implemented.
These are measures that governments and organizations need to take seriously. AI is evolving quickly, and faster each year, but this doesn’t mean we should ignore the importance of data protection. If we do, many organizations and innocent people will have to suffer the consequences. However, with stringent data protection strategies based on a clear understanding of every AI system put in place and how it relates to the law, many troubling situations can be avoided.
Cyberlocke is a comprehensive, full-service IT services provider that architects and implements efficient and secure solutions for enterprise customers and their data centers. We specialize in security, cloud, managed services, and infrastructure consulting. Contact Us today to learn more.