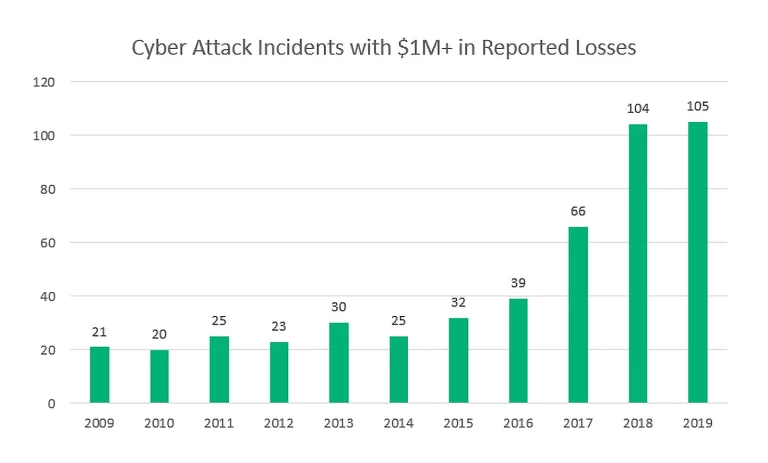
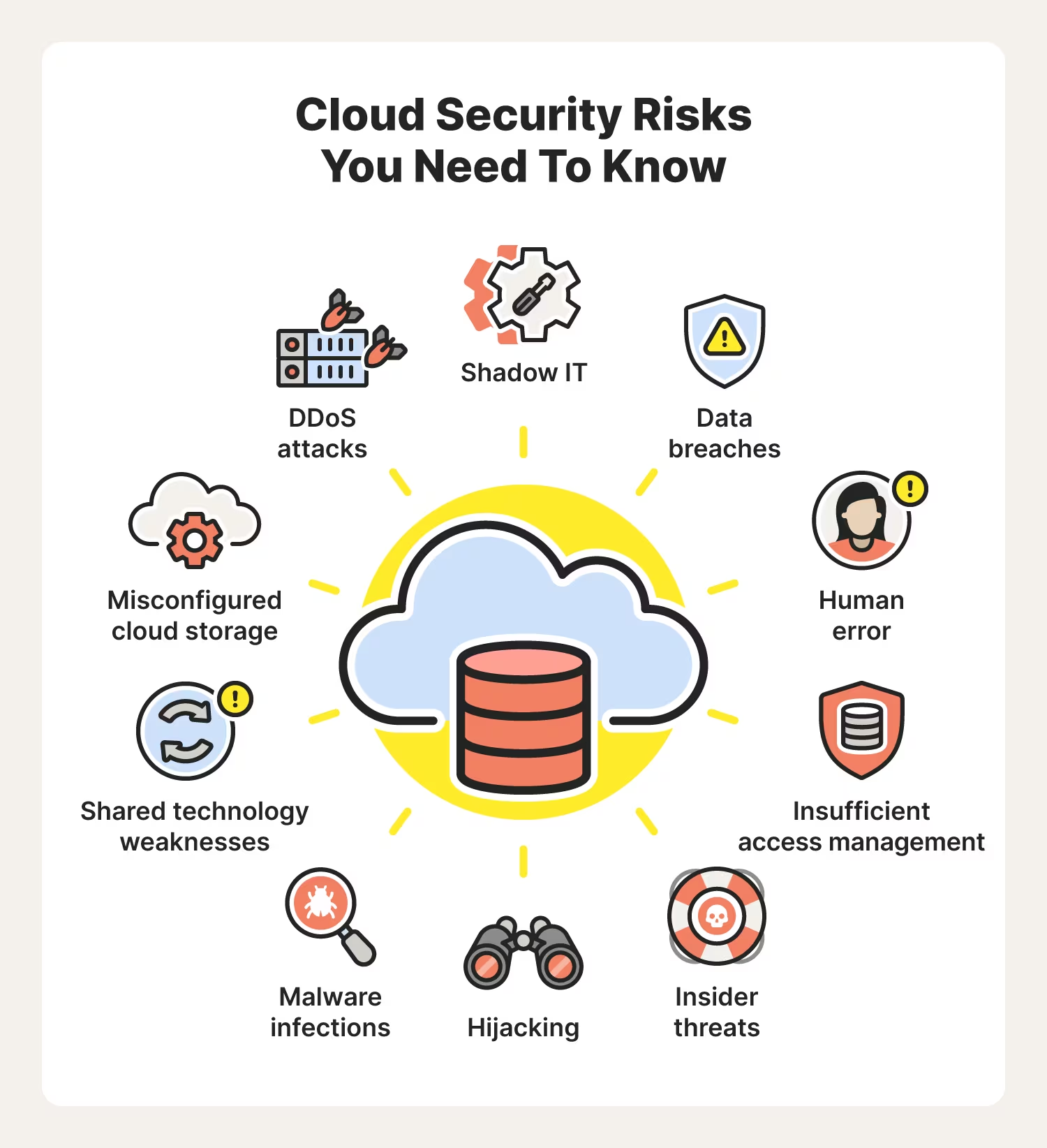
Responding to a Cyberattack, Step-by-Step
When you notice that a cyberattack has occurred, you need to be able to respond immediately. This will give you the best chance of preventing any further (and perhaps more serious) damage. However, the way you respond has to be systematic, both to ensure that the hacker can’t continue to jeopardize your data and also to prevent another attack from occurring in the future.
Before initiating the first response, you need an adequate incident response team. This should include all relevant internal stakeholder groups, such as:
- A technical team to investigate the breach
- HR and employee representatives if the breach affects employees
- Intellectual property experts who can minimize brand impact or recover stolen IP
- Data protection experts where personal data is involved
- Public relations representatives
It may also be necessary for external representatives to get involved, in cases where the internal teams don’t have sufficient capacity or capability. The incident team should, moreover, include representatives from the company’s legal team. A cyberattack may have legal implications, in which case legal counsel is of paramount importance.
Business leaders should check whether losses are covered under existing insurance policies as well and if so, then contact the insurer about the breach.
Now let’s describe all the necessary steps you need to take in response to a cyberattack.
1. Secure Your Systems and Ensure Business Continuity
First, you want to secure the IT systems so you can contain the breach and ensure it is not continuing. This might mean you need to temporarily isolate or suspend a compromised section of your network or possibly even the whole network. This can be disruptive and costly, of course, which is why you need to have a plan that allows for business continuity in case a part of a network is compromised.
You also need to know how and when the breach was detected and if any other systems have been compromised. You should have measures in place that allow you to detect intrusions immediately.
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Investigation
You next need to understand all of the facts pertaining to the breach, its effects, and the necessary remedial actions. You should decide who will take the lead on the investigation and make sure that they have all the appropriate resources to complete the task effectively.
If an employee has potentially been involved in the breach, then the investigation will also need to take into account any relevant labor laws. The investigation team should consult HR representatives as well.
Furthermore, the investigation team has to make sure to document all the steps they take. This way, it can feed back its findings into the policies and procedures that constitute the incident response plan. This documentation can also be used to educate employees about what occurred, so they are better equipped to be on the lookout for potential threats.
3. Manage Public Relations
Your incident response team will have to manage public relations following a cyberattack, especially if your organization is a consumer-facing one. Not all security breaches will become public, of course, but for many, this outcome will be inevitable. This will occur in instances where customers’ personal data has been compromised and enters the public domain, or where data protection legislation requires that affected individuals be notified.
You want to be timely in managing announcements to the public, as well as accurate, open, and honest in your messages. Managing public relations in light of a cyberattack is crucial for maintaining your brand image.
4. Address Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Some cybersecurity laws will apply universally across sectors, whilst industry-specific legislation is continuing to develop to target the most at-risk sectors, such as financial services, critical utilities infrastructure, and telecommunications.
In the U.S., legal and regulatory frameworks organizations should be aware of include the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (which focuses on the protection of critical infrastructure) and the Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity.
Meanwhile, all organizations handling EU data should pay attention to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It includes a mandatory obligation for organizations across all sectors to inform the relevant data protection authority of any security breaches, including accurate information about how they occurred, their impact, and what remedial actions were taken.
As already mentioned, some legislation may require that individuals affected by the breach are notified within a certain time frame. This becomes difficult, of course, if your company has millions of customers. Nonetheless, if it’s possible for so many individuals to be affected by a data breach, you need to be able to accurately identify (as far as possible) who has been – or could be – impacted.
6. Incurring Liability
Unfortunately, incurring some form of liability in light of a cyberattack is often unavoidable. Some ways you could an incur liability include:
- Non-legal liability: blackmail attempts, theft, ransomware, ex-gratia payments
- Regulatory liability, such as fines, which may vary depending on the sector your business operates within
- Litigation for breach of statutory obligations, breach of contract, breach of equitable duties, and negligence
The legal, financial, and operational consequences following a breach can be severe, however, as we have seen, there are many proactive steps you can take to mitigate the impact of a cyberattack and the risk of one before it occurs.
Every organization should carry out an in-depth and systematic assessment of its current processes and procedures, identifying what needs to be protected and what the specific risks are. Following that, a response plan should be put in place, as well as a strategy for educating employees about the fundamentals of cybersecurity.
Cyberlocke is a comprehensive, full-service IT services provider that architects and implements efficient and secure solutions for enterprise customers and their data centers. We specialize in security, cloud, managed services, and infrastructure consulting. Contact Us today to learn more.