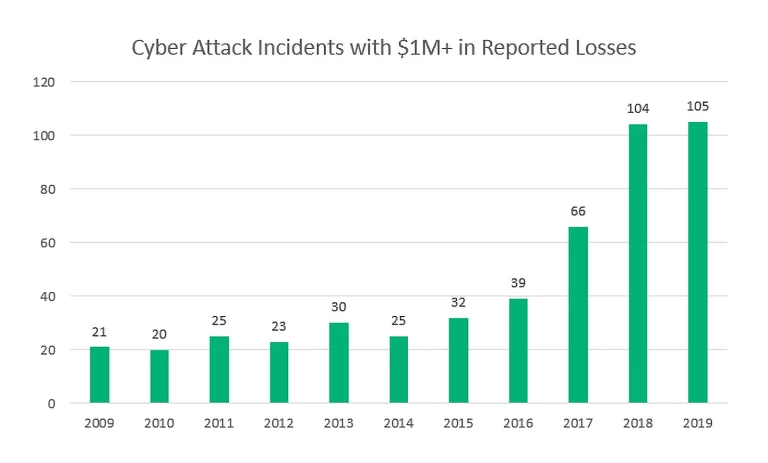
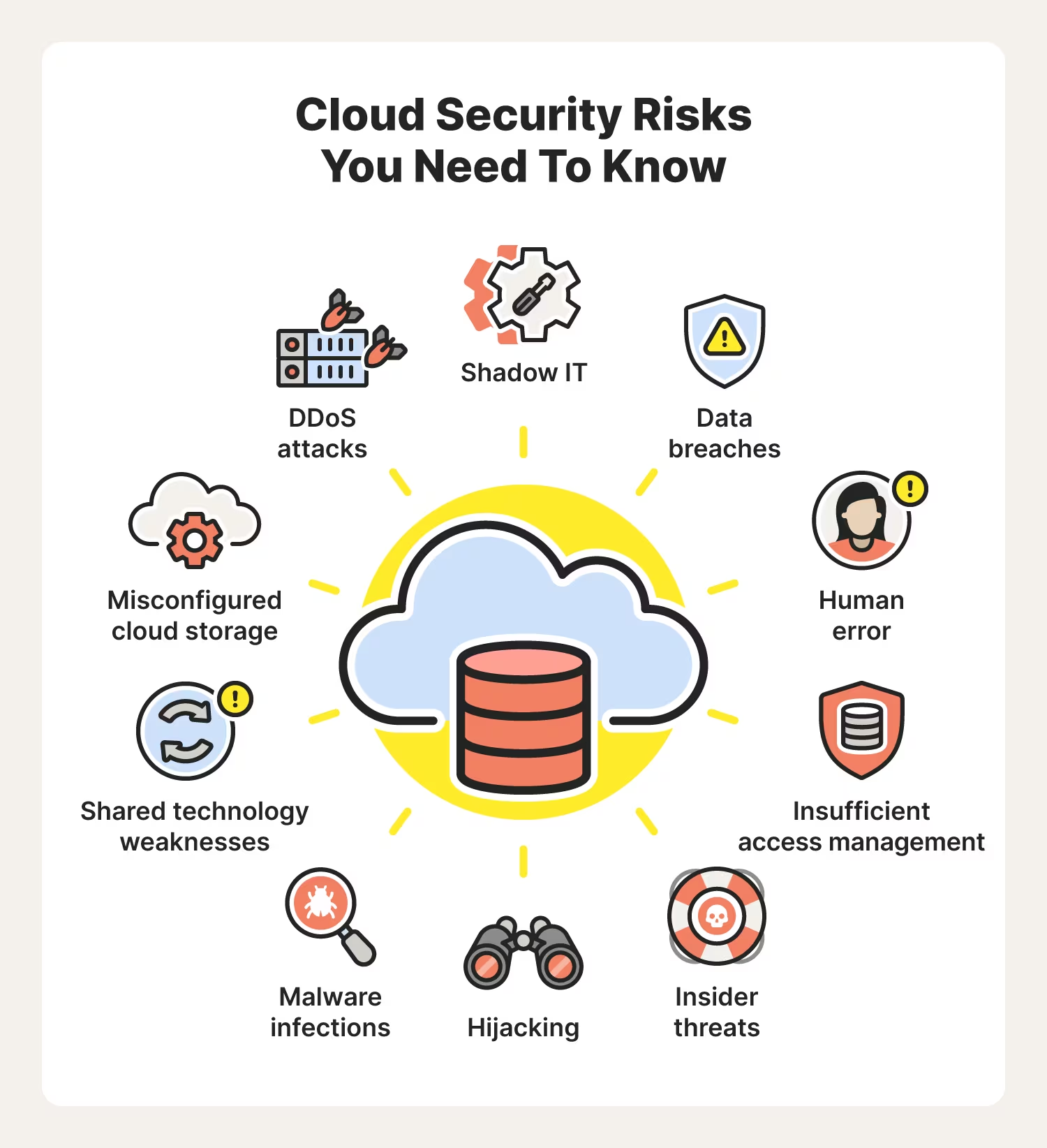
Maybe you’re reading this article on your phone. Swipe over to your home screen and take a look at how many mobile apps you have. The average person has 40 apps installed on their phone. That adds up to a lot of opportunities for cybercriminals to hack into.
As of the first quarter of 2021, there were 3,335 free and paid mobile applications in the Google Play store. 63% of those apps had known security vulnerabilities and each app had 39 vulnerabilities on average. So-called secure financial apps were near the top of the list with vulnerabilities seen in 88% of banking, 84% of budgeting, and 80% of payment apps.
One mobile app that likely avoided potential security vulnerability issues is the Bumble dating app. A security researcher used fake dating profiles to execute a ‘trilateration’ attack test on Bumble. It found a vulnerability that would enable attackers to pinpoint other users’ precise location and where they live. Luckily, Bumble was made aware of the issue and quickly deployed a fix, but it served as an example of how easily app vulnerabilities can be manipulated.
Vulnerabilities with Apps are an Ongoing Threat
Consumer mobile apps like Bumble are just one small section of the many applications out there that are facing increased vulnerability. Enterprise apps have seen a heightened risk of cyberattacks that is partly due to the rise of cloud-based apps, such as Zoom and Salesforce, from more employees working remotely.
Cybercriminals are becoming savvier and cyberattacks on applications have grown. 72% of organizations suffered at least one breach from an application vulnerability in the past 12 months. Enterprises face mounting pressure to launch the latest and greatest apps and outpace the competition. Yet this means that many apps go to market before they are ready and have the proper security protocols in place.
A Forrester report on the State of Application Security found that web applications are the most common form of external attack. This includes SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and remote file inclusion. The report predicts that applications will remain as a top attack due to the ongoing growth of open source and the continuing usage of containers that tend to have many code and configuration vulnerabilities.
Defining App Vulnerabilities
An app vulnerability is a flaw in the application system that is exploited by cybercriminals and as a result, the security of the application is compromised. This exploitation could expose the application to the ‘CIA triad’ of confidentiality, integrity, and availability that are integral to an organization’s security infrastructure.
App vulnerabilities can take many forms. The top application security challenge facing organizations is bad bots. 44% of respondents to The State of Application Security in 2021 report said that bot-based attacks are the most likely contributor to successful security breaches resulting from application vulnerabilities in the past 12 months. Software supply chain attacks (39%), vulnerability detection (38%), and securing APIs (37%) were also listed as application security-related challenges facing organizations.
Often poor credentials management is what opens applications up to attacks. When a user logs in to an app with an ID and password, that information is verified by comparing it to credentials in the app’s database. That information is often stored in plaintext or weak encryption databases that expose the app to vulnerabilities.
How to Mitigate App Vulnerabilities
Among security decision-makers, 28% say that improving application security capabilities and services is a top tactical IT security priority in the coming year. The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a nonprofit that works to persuade business executives and corporate boards of the need for effective vulnerability management. The OWASP Top 10 is a list of the most prevalent and critical application vulnerabilities. Cross-site scripting (XSS) and injection have made the list since it was first released in 2003. XSS vulnerabilities are present in two-thirds of all applications.
The best way to mitigate app vulnerabilities is to implement security into the app development lifecycle. 21% of security decision-makers say their firm will prioritize building security into development processes. AppDev and DevOps automate everything from code build to service deployment and cybercriminals also use automation to launch their attacks. That’s the benefit of integrating security into app development because of automation.
At Cyberlocke, we partner with F5 to bring our clients a unique integration into their app security. The F5 products and services guard all your apps against constantly evolving security threats to accelerate digital transformation and protect strategic business outcomes. Plus, F5 is backed by 24/7 access to Cyberlocke’s security experts.
Cyberlocke offers industry-leading IT services that support efficient and secure operations To drive productivity, increase security, and improve business value. Let’s talk.