Earlier this year, global sports retailer Decathlon decided to leave its onsite data centers behind and make the migration to the cloud. Decathalon is experiencing rapid growth and needed to scale up its cloud operations to provide a more secure, flexible, and integrated platform for its products and services. They are seeing results with decreases in IT costs and increases in efficiency.
Decathalon is just one of a number of companies that have realized the benefits of cloud services this year. The pandemic accelerated organizations to prioritize optimizing their cloud applications to ensure long-term resiliency. 70% of organizations using cloud services today plan to increase their cloud spending in the wake of the disruption caused by COVID-19.
The Cloud Services Landscape
The major benefit of the cloud is that it can be scaled to meet an enterprise’s demands for IT, personnel, operations, and other key business areas. And in 2021, that scale is only going up with 85% of enterprises planning to adopt a cloud-first principle by 2025.
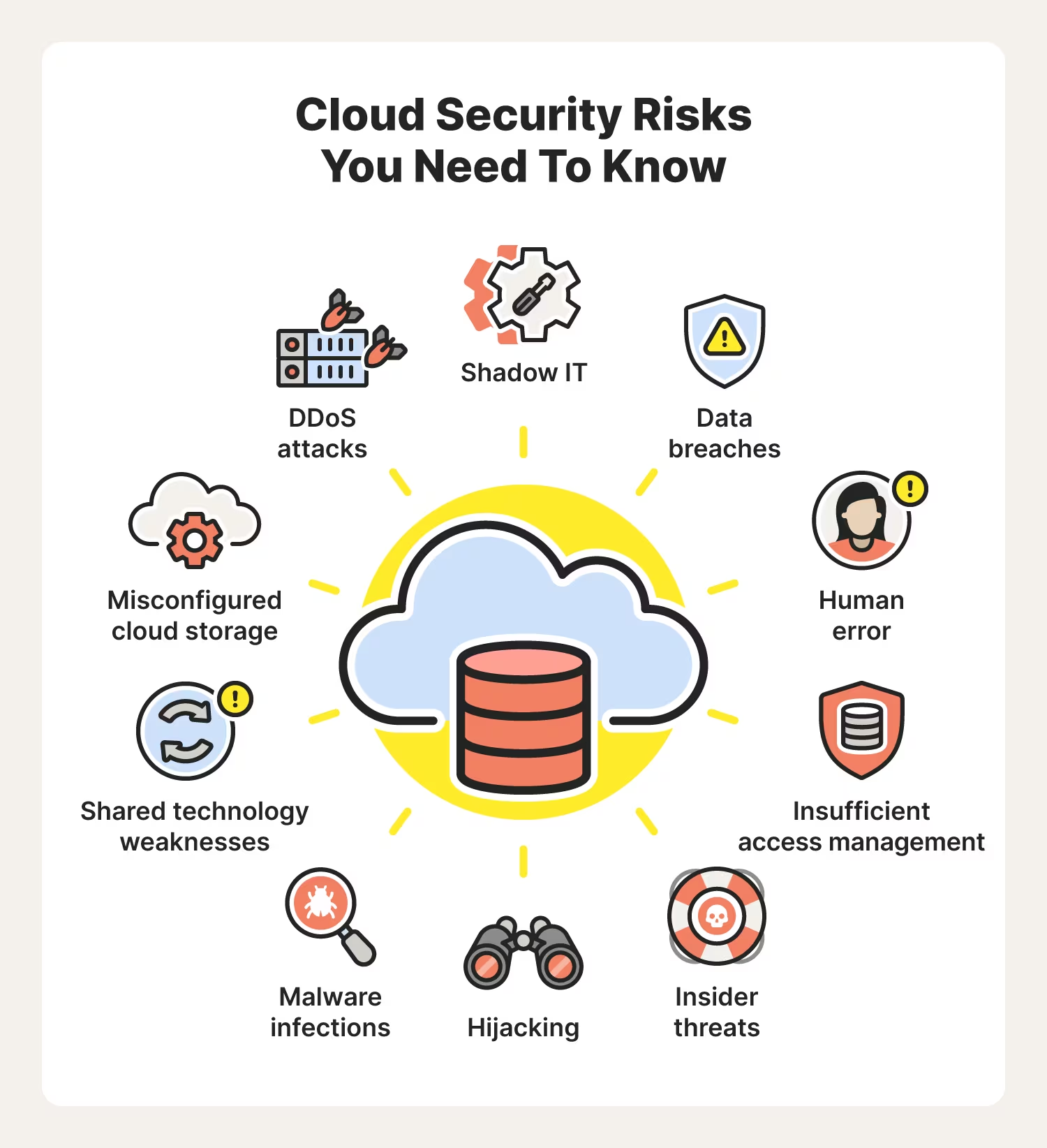
Although the pandemic is the major driver of cloud migration, many companies are also making the move this year because of the security benefits. Almost 9 in 10 businesses believe their data is safer in cloud-based solutions. Enterprises find that the most useful cloud features are encryption (43%), multi-factor authentication (42%), monitoring (39%), and anti-malware (39%).
A key trend that has been happening over the last few months is that companies are assessing their cloud needs and choosing a mix of public and private cloud services or adopting a hybrid model. Needs can differ based on regulatory demands, geographic preferences, or specific feature requirements. Accenture found that 93% of enterprises have built up to a multi-cloud strategy and 87% have already adopted hybrid cloud strategies. The valuation of the hybrid cloud industry is expected to inflate from a valuation of $44.6 billion in 2018 to almost $100 billion by 2023.
Popular Uses of Cloud Services
There are three general areas that organizations rely on cloud capabilities for: software as a service (SaaS), infrastructure as a service (IaaS), and platform as a service (PaaS). SaaS was the first cloud service on the scene and IaaS and PaaS later emerged to align with modern business objectives.
Other ‘as a service’ cloud models have developed to meet organizations’ growing demand in the world’s new normal. These are some of the popular cloud uses that have emerged:
- Workstation as a Service (WaaS): In today’s work from anywhere world, WaaS gives employees what they need, when they need it, and on any device. What were historically on-premise tasks can now be carried out remotely with the security of full backup capabilities and anti-virus software. The WaaS global market size is projected to grow from USD 8270.3 million in 2020 to USD 14880 million by 2027.
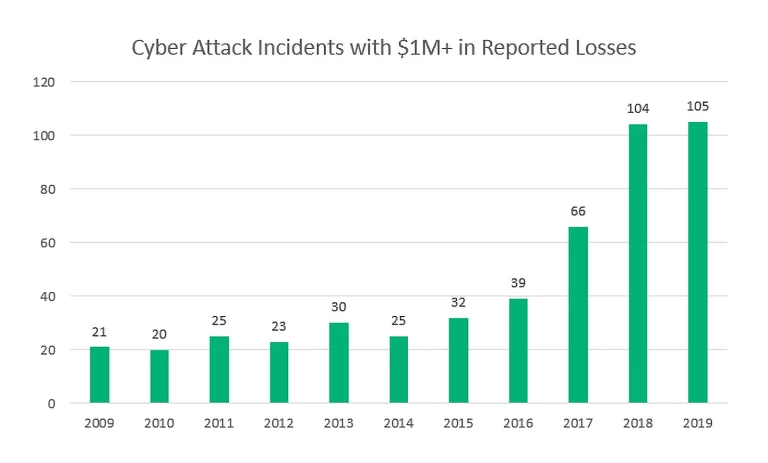
- Disaster Relief as a Service (DRaaS): Having a disaster recovery plan is important with the average cost of cybercrime for an organization hovering around $13.0 million. Many organizations are adding an automated disaster relief strategy with DRaaS to respond quicker and significantly reduce the recovery time from these types of disruptions or others such as natural catastrophes or power outages.
- Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS): Global spending on AI is forecast to grow from $50.1 billion in 2020 to more than $110 billion in 2024. AIaaS allows businesses to experiment with AI and test different algorithms without the risk of making a large investment in it. They can scale their AI techniques at a fraction of the cost of doing it in-house.
Cloud Applications on the Horizon
There is no doubt that cloud services are here to stay and will continue to scale in their number of features and offerings as well as their technological advances.
These are three cloud applications trends that will continue to progress in 2021 and beyond:
- Containerization: Several cloud providers offer container applications and demand for these is expected to grow. Gartner predicts that by 2023, more than 70% of global organizations will be running more than two containerized applications in production which is up from less than 20% in 2019. Containers are deployed on top of the cloud application layer and can help address the management and operational concerns associated with a hybrid cloud.
- Human cloud: Independent work is growing fast at 34% year-over-year. The human cloud houses talent on digital platforms for these on-demand workers. It allows potential employers to build their staff with access to a range of gig workers for projects. Examples include companies like Upwork for freelancers or Uber for drivers.
- Sustainable cloud: Organizations will continue to seek out companies that offer products and services that align with their vision and values, especially when it comes to sustainability. The good news is that public cloud migrations can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 59 million tons per year. This is the equivalent of having 22 million fewer cars on the road and a great incentive for companies to make the switch.
Cyberlocke offers industry-leading IT services that support efficient and secure operations To drive productivity, increase security, and improve business value. Let’s talk.