What is Confidential Computing?
Confidential computing is a concept – and type of cloud computing technology – that can substantially help to enhance the overall security of your enterprise. This new way of encrypting data can keep your sensitive data secure in a way that is not achievable with older technologies.
Let’s explore what confidential computing is in greater detail, as well as highlight its uses and benefits.
The Basics of Confidential Computing
Confidential computing involves encrypting data in memory to limit access, ensuring that data in use is protected. The concept is promoted by the Confidential Computing Consortium (CCC), a group of organizations that aims to build tools supporting data protection in cloud computing environments. The consortium is made up of hardware vendors, cloud providers, and developers, including Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Intel.
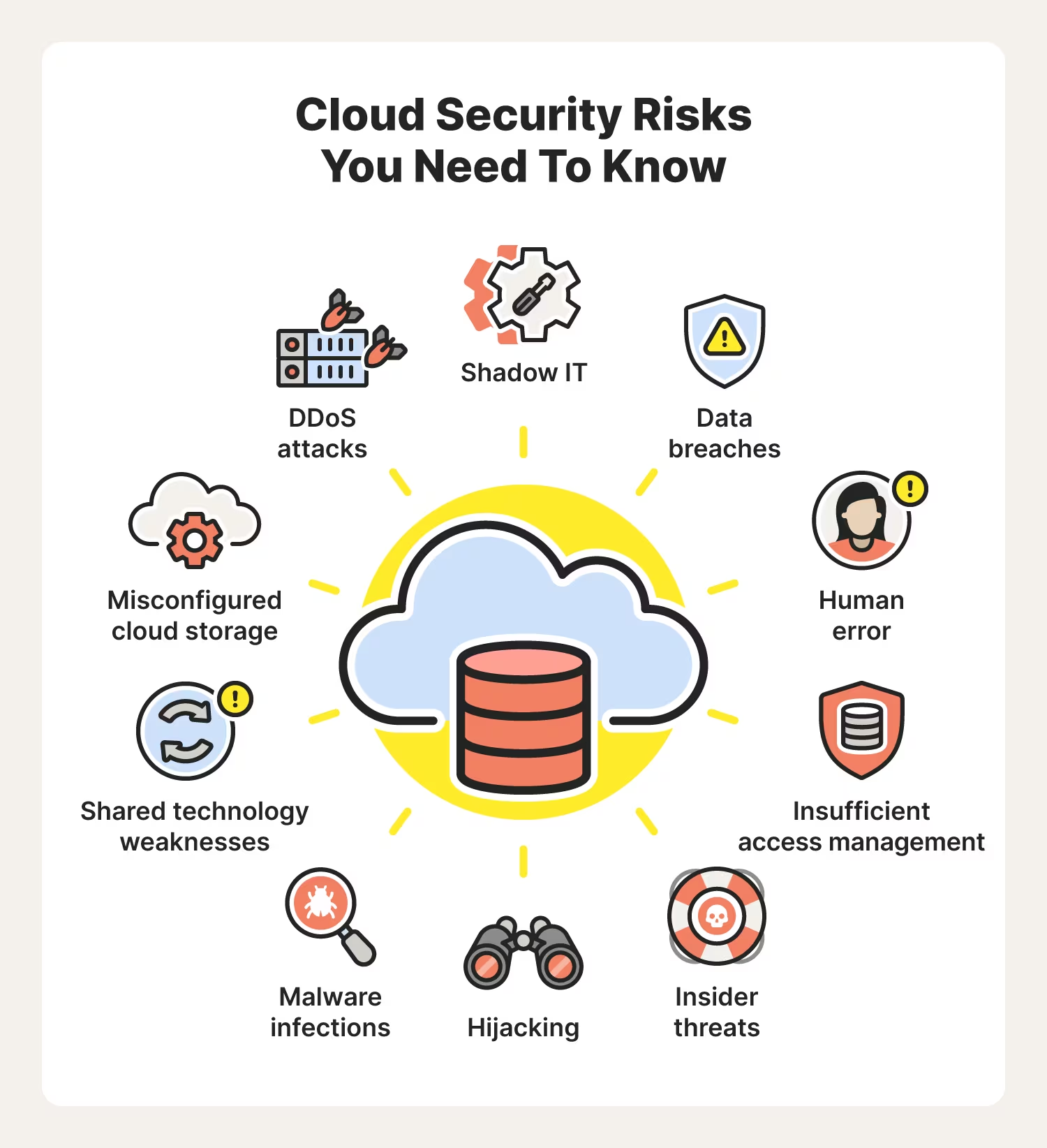
Confidential computing protects data against risks such as malicious insiders, network vulnerabilities, or any threats to hardware or software-based technology.
In terms of encryption, you would normally encrypt data when it’s at rest (in storage and databases) or in transit (moving over a network connection). But this data is no longer encrypted when in use.
The CCC focuses on protecting data while it’s in use – specifically when the data is processed in memory. This minimizes the exposure of any private information. The result is that the data is only unencrypted when a code on a system allows a user to access it. The data is hidden from the cloud provider as well, which further improves the level of security.
Confidential computing protects data in use by carrying out computation in a hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). These are secure and isolated environments within a CPU that stop unauthorized access or modifications of applications and data while in use.
The TEE is secured using embedded encryption keys, with the keys accessible to authorized application code only. If malware or some other unauthorized code attempted to access the keys, the TEE would deny access to the keys and cancel the computation. This increases the security assurances for organizations that deal with sensitive and regulated data.
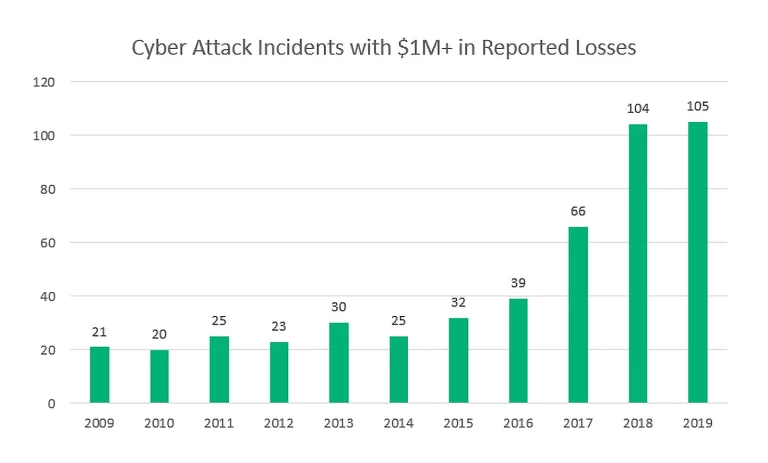
Cloud computing is, therefore, especially appealing to organizations that handle data like Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data, or health information. Threats that target the confidentiality and integrity of this data need to be mitigated as far as possible.
The Uses and Benefits of Confidential Computing
Using confidential computing entails a number of uses and benefits. These include:
- Protecting sensitive data, even while in use.
- Moving sensitive or highly regulated data sets from an inflexible, expensive on-premises IT infrastructure to a more flexible and modern cloud platform.
- Protecting intellectual property. Confidential computing isn’t restricted to data protection. The TEE can also protect proprietary business logic, analytic functions, machine learning algorithms, or entire applications. Martin Reynolds, a technology analyst at Gartner, notes this is useful when it comes to the analytics applications and algorithms used when trading stocks: “You don’t want me to know what stocks you’re trading, and I don’t want you to know the algorithm. In this case, you wouldn’t get my code, and I wouldn’t get your data.”
- The potential to collaborate securely with partners on new cloud solutions. Your company’s team could combine its sensitive data with another enterprise’s proprietary calculations to formulate new solutions. And you could do all this without sharing any data or intellectual property that you don’t want to share.
- Eliminating worries when choosing cloud providers. Confidential computing allows you to choose cloud computing services that meet your technical and business needs, without worrying about storing and processing customer data, proprietary technology, or other sensitive assets. To reiterate, when your data is being processed in the TEE, it will be invisible to even your cloud provider. This approach can also help alleviate any competitive concerns if your cloud provider offers competing business services.
- Protecting data processed at the edge. Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that brings applications closer to data sources like IoT devices and local edge servers. If you use this framework as part of distributed cloud patterns, you can better protect the data application at edge nodes with confidential computing.
- Ensuring that your data complies with legislation such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which you will need to comply with if you handle any EU customer data. Not complying with regulations like GDPR can entail legal fines and penalties, as well as an increased risk of cybersecurity incidents and damage to the company’s reputation. Therefore, it’s best to take as many steps as you can to avoid violating legislation that deals with data protection.
- Making sure that data in use is protected when migrating workloads to different environments.
- Allowing developers to create applications that can be moved across different cloud platforms.
Most confidential computing today runs on Intel servers (such as the Xeon line) with Intel Software Guard Extension (SGX). However, some research has shown that Intel SGX can be vulnerable to side-channel and timing attacks. Fortunately, however, TEEs aren’t restricted to Intel hardware. OP-TEE is a TEE for nonsecure Linux Kernels running on Arm Cortex-A cores, while Microsoft’s Virtual Secure Mode is a software-based TEE implemented by Hyper-V.
As evidenced by the big corporations part of the CCC, it is clear that confidential computing is being seen as a viable way to better protect data in all its forms.
Cyberlocke is a comprehensive, full-service IT services provider that architects and implements efficient and secure solutions for enterprise customers and their data centers. We specialize in security, cloud, managed services, and infrastructure consulting. Contact Us today to learn more.