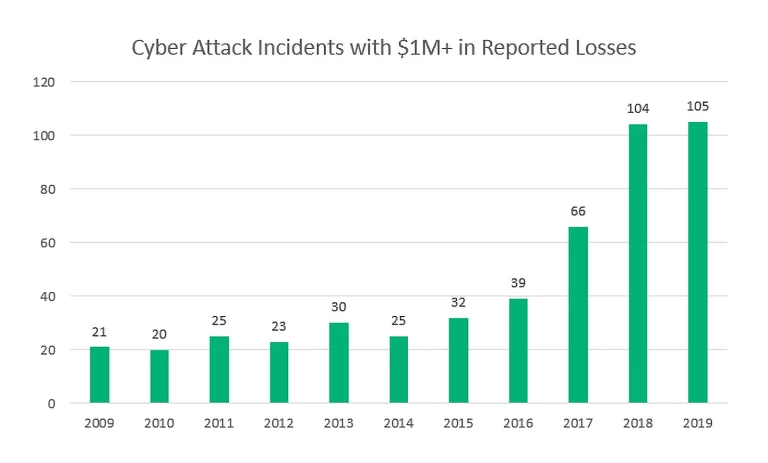
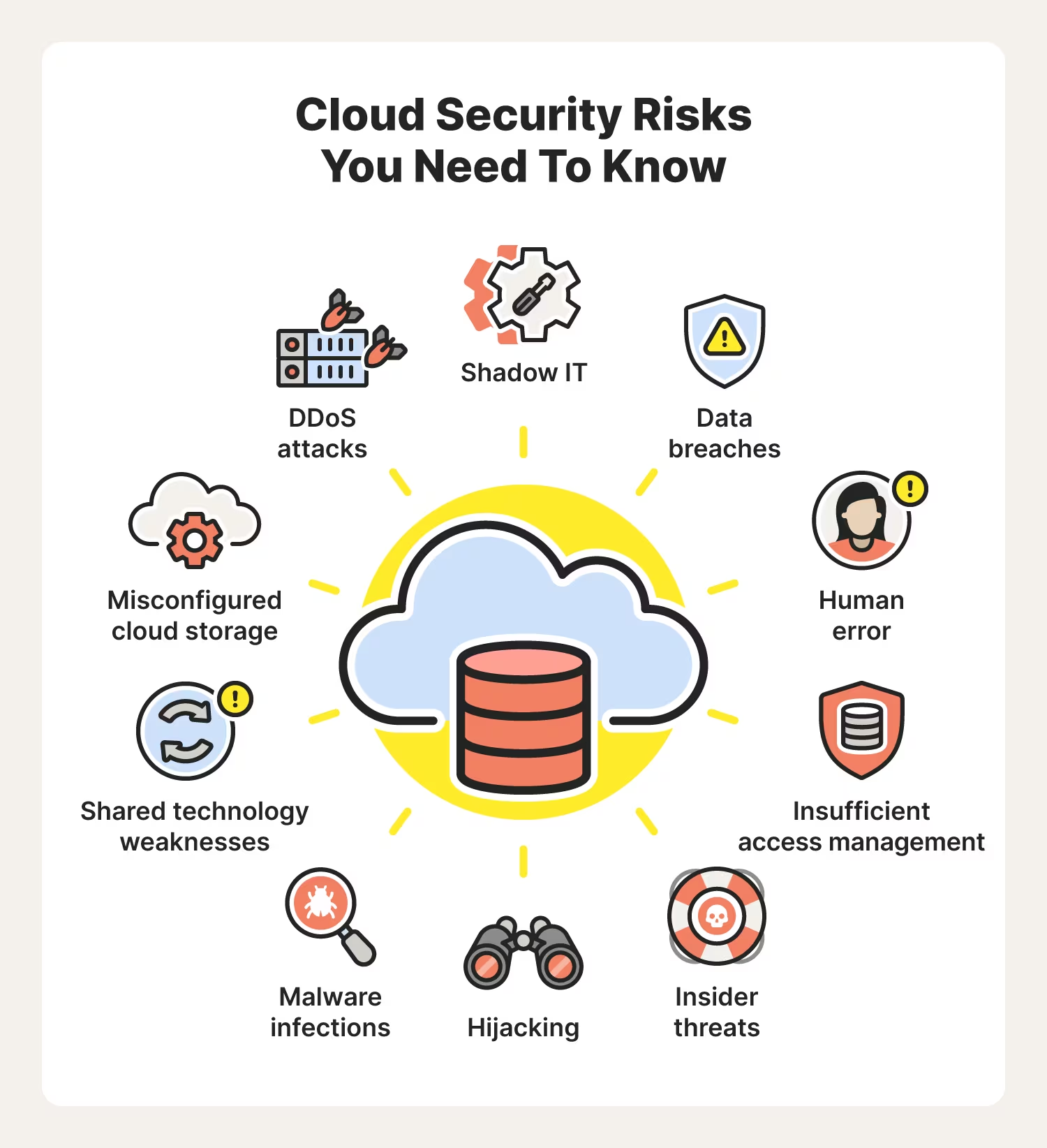
Dealing with a data breach can often be a logistical nightmare, causing major interruptions to business while the issue is rectified. However, it’s not just inconvenient and stressful for an organization to have to deal with a major security incident; it can result in significant financial losses as well.
There are many different types of costs associated with data breaches. This post will describe what these are and, in cases of a major data breach, how devastating the consequences can be. Knowing all of the potential costs of a data breach should provide any enterprise with the incentive to make its cybersecurity strategy a top priority.
Direct Financial Loss
There are direct costs associated with data breaches that you need to be aware of. These relate to the costs involved in the detection, notification, and rectification of a data breach.
The immediate financial impact you will see after a data breach will typically be on sales revenue. This is due to the network downtime and losses in productivity that will occur. Moreover, after a data breach, the company share will likely drop. Your enterprise may need to make large payments to legal services to control the fallout of litigation. These costs can then increase if you need to get investigative consultancy firms involved to find out the root cause of the data breach.
You will incur further costs when putting in place a post-breach response, such as creating and implementing an emergency call center for affected customers. It may also be necessary to finance public relations activities, which may include financially reimbursing customers for any losses they experienced.
Other financial costs include breach containment and damage control, as well as newly required spending on security hardware and software.
In 2018, UK-based TSB Bank suffered a week-long disruption to its service, the cost of which nearly totaled £200m. While not caused by a data breach, this scenario shows how a cyber attack that compromises or exposes private data could incur similar costs.
Many cyber criminals will also steal funds from organizations through ransomware, with demands ranging from a few thousand dollars to over one million. Nearly half of ransomware attacks involve stealing data and include the threat of releasing the protected data.
Notable examples of ransomware include SamSam, Ryuk, and LockerGoga. Hackers will target specific systems – typically critical infrastructure – with ransomware attacks, putting them in a position to demand large sums of money.
If you become a victim of such an attack and don’t pay up, you can lose critical business functions and data. To avoid the threat of extortion and data loss, then, you need robust cybersecurity protocols that can protect you from ransomware.
Indirect Costs: A Loss of Reputation, Competitiveness, and Business Opportunities
Another major cost of a data breach is that customers may lose trust in your organization’s ability to maintain the confidentiality of their data. If this happens, your customers may move to a competitor. Indeed, it can be hard to regain the reputation you had before a data breach, especially when the breach is a major security incident, exposing sensitive customer information in the process and resulting in cases of financial theft and identity fraud.
A data breach may also mean that your business misses out on lucrative business opportunities. Companies that would otherwise be interested in working with you might see the data breach as a sign that you don’t have adequate cybersecurity protocols in place. After all, no business wants to risk compromising its own private data.
Furthermore, investors may be less likely to buy the company stock, which will result in a reduced market share and restricted growth. You may find, as well, that employees decide to leave the company due to its declining reputation. There will be further indirect costs, too, such as having to pay more for your business insurance.
How to Avoid the Costs of a Data Breach
The key to avoiding the various direct and indirect costs associated with a data breach is to invest in robustly secure cybersecurity technology. To maintain overall security, an organization should utilize:
- A managed services provider (MSP)
- AI, especially in the context of threat detection software and cloud security
- Next-generation firewalls
- Encryption safeguards on sensitive or valuable data, ideally enforcing encryption at every layer of the IT system
- An incident response team and plan
- Endpoint security software on all company assets
- A tried and tested business continuity plan, which should include every step that needs to be followed when a disaster like a total system outage or ransomware breakout strikes your organization
- Regular training initiatives, so that all employees are aware of what steps need to be taken to ensure data security, the consequences of a data breach, and the repercussions to them should they fail to achieve compliance
A single data breach can spell disaster for an organization, no matter how large, reputable, or profitable it is. But by investing in a solid cybersecurity team and technology, you can avoid data breaches from occurring in the first place. In the long run, this will always be a worthwhile investment.
Cyberlocke offers industry-leading IT services that support efficient and secure operations To drive productivity, increase security, and improve business value. Let’s talk.