Every year, hackers develop new techniques for compromising enterprises’ vulnerable data. This calls for a re-evaluation of cybersecurity best practices and the implementation of the latest technology to counteract these attempts. 2021 has seen an influx of novel scams, attacks, and breaches, as well as a large number of these activities taking place. Part of the reason for this has been the ongoing pandemic, which has meant many of us are spending more time on our devices.
Fortunately, we’ve kept track of the best cybersecurity protocols that businesses need to protect sensitive customer and employee information. This includes having excellent cloud security in place.
Let’s take a look at some of the most significant cyberattacks that have taken place this year and how they can be prevented or mitigated.
Significant Cyber Attacks in 2021
The Centre for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS) has outlined the most serious cyber attacks that have occurred in the past year, with a focus on attacks on government agencies and high tech companies, or economic crimes with losses of more than a million dollars. Some examples include the following:
- January 2021: Hackers breach one of the data centers of New Zealand’s central bank.
- January 2021: Hackers linked to Hezbollah breached telecom companies, hosting providers, and internet service providers in the Middle East, US, and UK for intelligence gathering and data theft.
- February 2021: 10 members of a cybercriminal gang were arrested for tricking telecom companies into assigning celebrities’ phone numbers to new devices and then stealing more than $100m worth of cryptocurrencies in the process.
- February 2021: A Portuguese-speaking cyber criminal group accessed computer systems at a division of Oxford University research COVID-19 vaccines and are thought to be selling the data they gathered to nation states.
- March 2021: Chinese government hackers targeted Microsoft’s enterprise email software to steal data from more than 30,000 organizations across the globe. These organizations included government agencies, law firms, defense contractors, and policy think tanks.
- March 2021: Suspected state hackers targeted the Australian media company Nine Entertainment with ransomware, disrupting live broadcasts and print production systems.
- April 2021: Malware triggered an outage for airline reservation systems, causing the networks of over 20 low-cost airlines across the world to crash.
- May 2021: The Colonial Pipeline, the largest fuel pipeline in the US, was the victim of a ransomware attack.
- May 2021: Brazil-based JBS, the world’s largest meat processing company, was the victim of a ransomware attack, carried out by the Russian cybercrime group REvil.
- June 2021: Hackers linked to Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service installed malicious software on a Microsoft system, enabling hackers to access accounts and contact information.
- July 2021: Russian hackers exploited a weakness in Kaseya’s virtual systems/server administrator (VSA) software, allowing them to implement a ransomware attack on the network, affecting more than 1,500 small and medium-sized businesses.
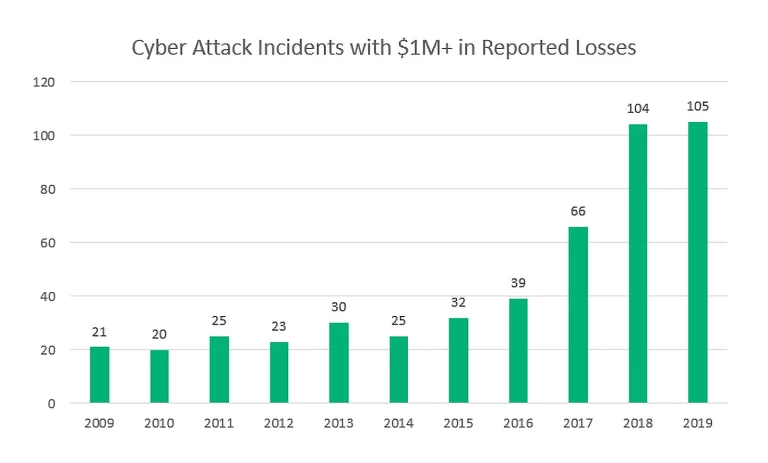
Cybercrime worldwide rose by 600% during the pandemic, with damages from cybercrime expected to cost $6tn in 2021 (up from $3tn in 2015).
Cybersecurity Best Practices in 2021
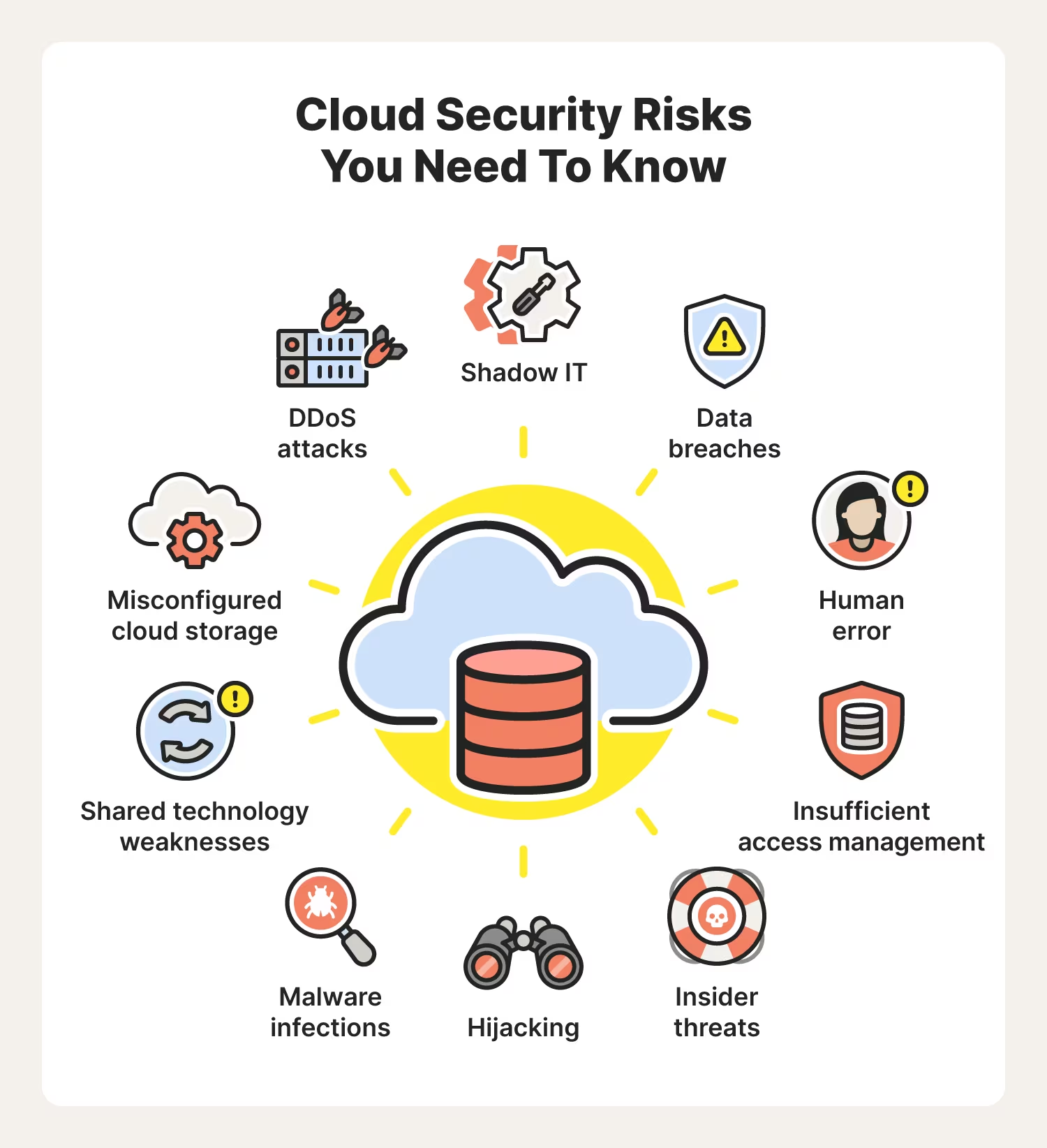
There are many steps that organizations of all sizes and types can adopt to enhance their cloud security (which is particularly vulnerable to cyber attacks), as well as overall IT security. Based on the kinds of threats described above, businesses should incorporate the following practices into their cybersecurity strategy:
- Many breaches involve credentials like passwords. For this reason, consider multifactor authentication (MFA), which will ensure hackers will be locked out of systems even if passwords are stolen or compromised.
- Employ third-party controls. Organizations are increasingly connected to third parties, such as external partners, suppliers, and customers. Protecting an organization means having cybersecurity controls in place for third parties that may have access to sensitive information, networks, or facilities. Best practices include limiting third-party access via the ‘least privilege’ approach, as well as monitoring the third party’s own cybersecurity controls.
- Create a hierarchical cybersecurity policy. Different departments in any organization will have varying cybersecurity needs. For this reason, it’s important to devise and implement a tiered approach to cybersecurity policy, so that customized policies can be applied to various departments and functions.
- Leverage managed services. To avoid the risk of falling victim to a cybersecurity attack, you need to be well-prepared, without taking shortcuts. For this reason, it’s helpful to leverage the expertise of a managed security services provider (MSSP). The advantages of utilizing MSSPs include reducing costs since you don’t have to train staff to have the most up-to-date knowledge on IT security – the MSSP will already be able to apply this knowledge. MSSPs also employ automatic detection and response, monitor privileged users (to prevent breaches from internal actors), and they will have 24/7 support for security incidents. This shifts a lot of technical burdens and workload pressure away from your organization. However, you do need to ensure you use a quality provider and understand the precise services you’ll be getting.
- Protect the home office. While the overall workforce was already shifting towards more remote working before the pandemic, 2020 completely changed the way we do business, pushing millions worldwide into home offices. This change presents a significant cybersecurity challenge. Insufficiently secured home offices are susceptible to data breaches. However, employees can keep an organization’s data assets secure by keeping confidential information away from other household members, closing all browsers and applications as well as disabling access to company materials when not working, and using a VPN for an additional layer of security.
With these recommendations in mind, organizations can effectively improve and maintain their IT security, stopping malicious actors from compromising their systems, as well as minimizing the damage should any attacks occur.